In this article, we’ll learn how to remove applications using Yum. YUM is an open-source command-line package manager used by distros using RPM Package. It stands for Yellow Dog Updater Modified.
It is available on Red Hat Enterprise Limited (RHEL), CentOS, Fedora, OpenSUSE, etc. which uses the RPM package manager. It is used for installing, updating, uninstalling, and querying packages.
Removing packages using the YUM command removes the package along with its dependencies, but some dependencies are not removed. In this article, we will be discussing how to uninstall packages using the YUM command along with its dependencies.
You will need sudo privileges, i.e. root access, in order to remove a package from your distribution. In this article, We are using Fedora 34 to run the Yum command, however, you can use any Fedora or CentOS version that uses this command.
Using the yum command to list Installed packages
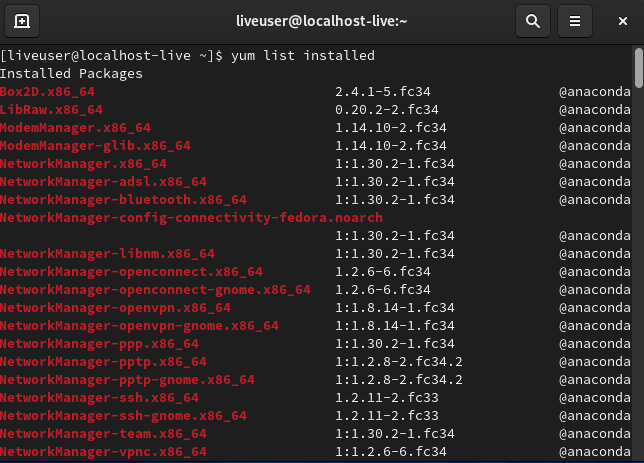
For uninstalling packages, you need to know the correct package name. To list all installed packages, run this command:
yum list installed
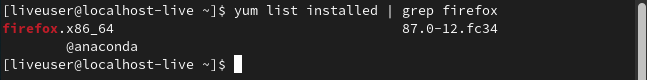
To search for a particular package, use the grep command:
yum list installed | grep <package_name>
Here, we have taken the package as Firefox,
To list all available and installed packages, run the following command:
yum list all
Uninstall packages using YUM
Now, we can find package names by using the above command. If you know the package name, you can uninstall a single package, multiple packages at once, or a group of packages using the following commands:
Removing package using YUM
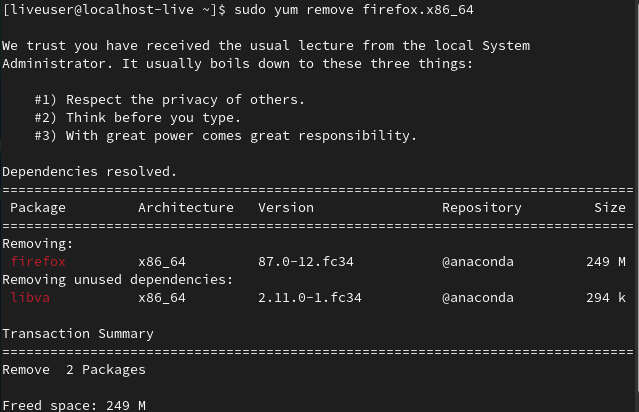
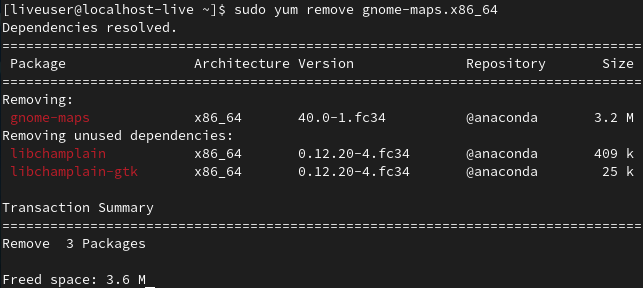
To uninstall a single package, run the following command:
sudo yum remove <package_name>
uninstalling Multiple packages at once using the YUM command with ‘remove’ subcommand
The above command of yum was useful for just removing a single package at a time. What if we need to remove a huge list of packages that we don’t want? Don’t worry, I have got you covered!
sudo yum remove <package_name1> <package_name2>
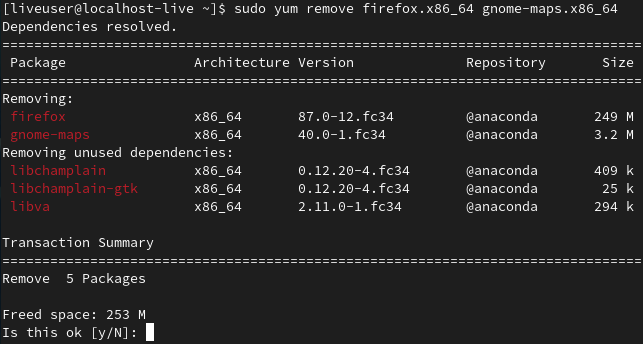
removing multiple packages using the erase subcommand of YUM
We can also use ‘erase’ subcommand instead of ‘remove’ to get rid of multiple packages.
Here’s the syntax,
yum erase <1st package> <2nd package> <3rd package> <x package>
Let me break the command down for you, then I will gloss over the process.
yum: The command-line tool for managing packages in YUM-based distributions.erase: This subcommand is used to remove specified packages from the system.<1st package>,<2nd package>,<3rd package>,<x package>: Placeholder names for the packages you want to remove. You have to replace these with the actual package names you wish to uninstall.
Installing or Uninstalling package groups using YUM command on Linux
Packages can be installed and uninstalled in groups by using the yum command.
Listing all the groups associated with the current system using YUM command
Before we go ahead and install or uninstall the packages, let’s first see how many groups are present in the current system we are dealing with.
The following command displays all the groups associated with the system,
yum groups list
Exploring the packages associated with the groups using YUM command
Now that we have learned how to display all the groups, we also need to know how to list all the packages that are under a group. We do so by running the following command,
yum groups info “name of the group”
Uninstall a package group using YUM command
To uninstall a package group, for example, ‘Performance Tools’, run the following command:
sudo yum remove @"<package_group_name>"
or
sudo yum group remove <group_name>
Remove packages using YUM along with dependencies
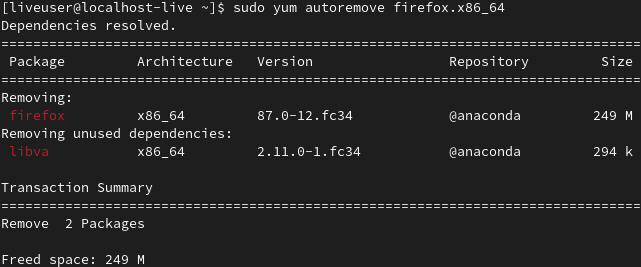
When a package is installed, some required dependencies are installed with it and stored. Uninstalling those packages also removes their dependencies, unless used by any other packages. Some dependencies are still left unused. To remove those dependencies, run the following command:
sudo yum autoremove <package_name>
If you want to remove these dependencies using the yum remove command, You can follow this method:
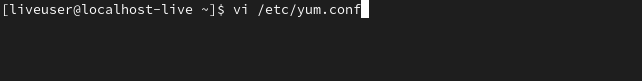
First, open the configuration file with any text editor,
vi /etc/yum.conf
Now insert the following line at the end:
directive clean_requirements_on_remove=1
Save and exit. Now all the dependencies will be removed using the yum remove or yum erase command without the autoremove command.
Conclusion
To summarize, getting rid of software packages on Linux via the YUM command is an easy task that entails recognizing the specific package or packages that you want to delete and then carrying out the necessary commands. This piece has directed you on how to view installed packages, eliminate one or more packages, uninstall groups of packages, and handle dependencies. By adhering to these guidelines and adjusting the yum.conf file to uninstall dependencies automatically, you can proficiently manage and tidy up your Linux system. Becoming proficient in these YUM commands is crucial for any Linux user looking to streamline their package management process.
Reference
Here’s the complete yum cheatsheet by Red Hat for your perusal.
What is YUM command?
YUM (Yellowdog Updater Modified) is a package management tool used in Linux systems, especially in distributions like CentOS and RHEL. It allows users to install, update, and manage software packages on the system.
How to remove a package using YUM?
To remove a package using YUM, you can use the command yum remove PACKAGE_NAME. This will uninstall the specified package from your system.
Can I remove packages with dependencies using YUM?
Yes, you can remove packages along with their dependencies using the yum remove PACKAGE_NAME command. YUM will automatically handle the removal of any dependencies that are no longer needed.
How to install a package using YUM?
To install a package using YUM, you can use the command yum install PACKAGE_NAME. This will download and install the specified package on your system.
How to list all installed packages using YUM?
You can list all installed packages on your system using the command yum list installed. This will display a list of all packages that are currently installed on your CentOS system.
What is YUM autoremove and how does it work?
YUM autoremove is a feature that allows users to automatically remove
