Creating and editing files is the most fundamental part of using a Linux-based system. There are different ways to edit files in Linux.
In this tutorial, we go over how to edit them on Linux systems. You can either use a GUI text editor, or you can do it using the terminal. This tutorial will cover the tools you can use to edit a file from the command-line.
Tools/Text Editors to Edit Files in Linux
We’ve already worked with multiple text editors like vim, nano, emacs, etc. Let’s look at these different tools one by one.
1. Vim Editor
Vim text editor comes by default in most Linux distributions. One feature that sets it apart from other editors is that it provides several modes for editing text. Basically, there are two modes, command mode and editing mode. Let’s take a look at both of the modes,
Entering The Command Mode
Vim starts in this mode by default, we can use arrow keys to move around the file, but we cannot just edit the text right away in this mode. Instead, you can execute various actions, such as copying, pasting, and deleting text.
To access Vim’s Command Line mode, press the colon (:) key while in this mode. This mode enables you to execute multiple commands, including saving files, finding text, and modifying configuration settings.
To check the version of your Vim editor, you can type the following in your shell:
vim -v
Open a file
To open a file or create a new file in the current directory using the Vim editor, use the command :
$ vim [filename]

If the file does not exist, this command will create the file for you.
Entering The Editing Mode
To start editing, simply press the “i” key while in Command mode. Editing mode allows you to make changes to the text in your file and navigate around using the arrow keys. You can also take advantage of a range of editing commands, including cut, copy, and paste, while working in Editing mode.
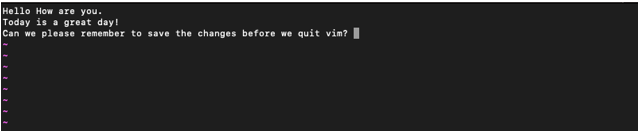
Edit file
To edit a file, you need to enter the insert mode—Press ‘i’ to do so.

The screen will look as shown above. You can notice ‘INSERT‘ written at the bottom. It indicates that we are in insert mode. You can type out some text to put in the file. You can now edit the file.
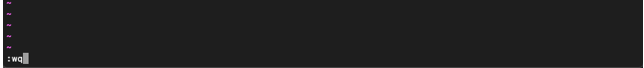
Save and Quit
To save your changes and quit vim, use the command :
:wq [enter]
To quit without saving your changes, use the command:
:q [enter]
Note on Vim and Vi Editor
Vi was the pre-cursor to vim. In fact, vim stands for vi improved. All of the vim and vi commands are fully compatible between each other. Here are some of the vi commands to edit a text file using the vi application.
Open a terminal window
Now, open a shell window by either using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + T or by finding the terminal application in your operating system’s application menu.
Editing Files in Vi
Type “vi” followed by the name of the file you wish to edit. For example, if the file you want to edit is called “example.txt”, type “vi example.txt” and press Enter. This will open the file in the vi app.
Press the “Esc” key
Press the “Esc” key to enter command mode. This mode allows you to enter commands for manipulating the text.
Move the cursor
Move the cursor to the desired location using the arrow keys on your keyboard. Alternatively, use the “h”, “j”, “k”, and “l” keys to move left, down, up, and right, respectively.
Editing the text in vi editor
Start editing the text by typing on your keyboard. The text you enter will be inserted at the current cursor position. You can also append text at the end of the file.
Saving the file in vi
To save the changes made to the file, press “:” followed by “w” and then “q”. This will write the changes to the file and exit from vi.
quitting the vi editor
To exit the editor without saving changes, press “:” followed by “q”.
2. Nano Editor
Nano usually comes pre-installed on most Linux distributions. To check the version of the nano which is installed on your system, use the command:
nano --version
If you need to install nano on your system, you can use the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nano
Open and edit a file
Now, open the file which you want to edit in nano, use the command :
nano [filename]
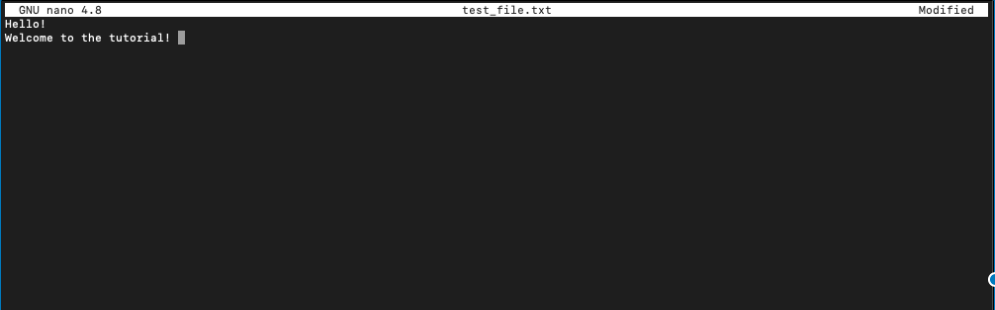
This command will open a screen where you can edit the contents of your file. Unlike Vim editor, you won’t have to enter insert mode to edit.
Save and Quit
You can see the options available in the nano at the bottom of the screen.

To save your changes and quit, use Ctrl + X.
The bottom of the screen will ask you if you want to save the changes.
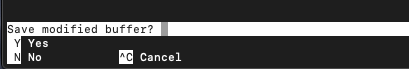
Press Y followed by enter if you want to save the changes otherwise, press N followed by enter to quit without saving.
To learn more about nano editor, refer to their official website.
Emacs editor
Emacs is one of the oldest and most versatile text editors available for Linux UNIX-based systems. It has been around for over 20 years. It is known for its powerful and rich editing features.
To install the Emacs editor on your system, use the command :
sudo apt-get install emacs
During installation, you will be prompted to confirm the installation.
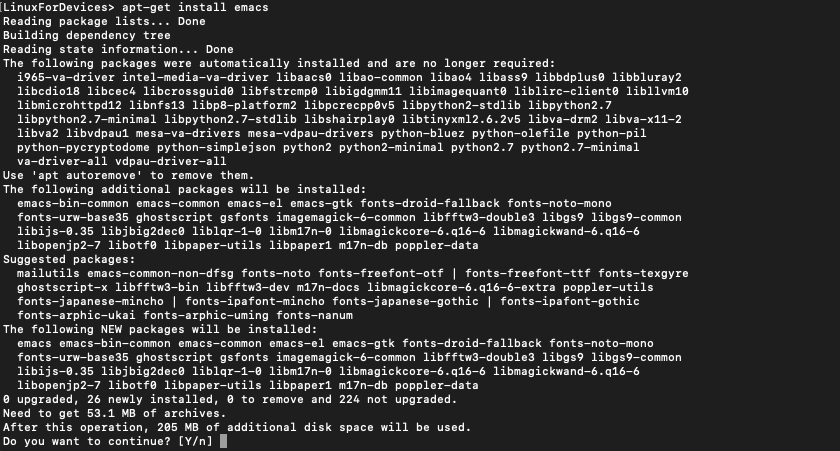
Press Y to continue.
After installation, you can check the version using the command :
emacs --version
Open and Edit a File
To open and edit a file using the command :
emacs -nw [filename]
Here -nw means no window. This makes sure that the editor window opens in the terminal itself.
This will open a screen that will look like this:
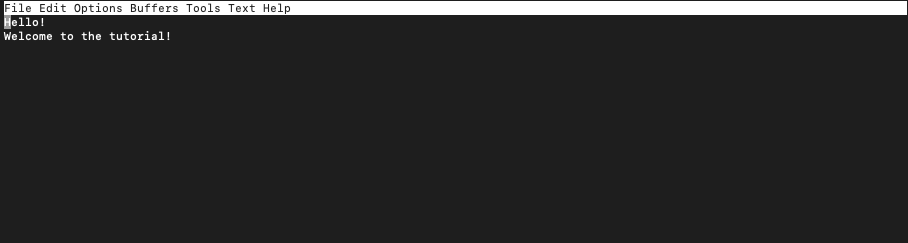
You can edit the content directly without entering any mode, like in the case of the nano editor.
Save and Exit
After editing, you can save your changes and exit using Ctrl + X, followed by Ctrl + C. The editor will ask you if you want to save before quitting Emacs.
If you only wish to save and not exit the editor, press Ctrl + X followed by Ctrl + S.
To learn more about emacs editor, refer to their official website.
Conclusion
The ability to modify documents within Linux is essential for anyone utilizing a Linux-driven platform.
This guide has discussed multiple ways to achieve this using the three distinct text editing programs—Vim, Nano, and Emacs—which can be employed to alter files through the terminal. Each editor possesses its own exclusive capabilities and instructions, making it crucial to select the one that best suits your needs.
Whether you are a novice or an experienced user, honing your skills in document modification on Linux will enable you to be more effective and prolific in your tasks. Therefore, continue to practice and delve into the expansive realm of Linux-oriented platforms. To learn different ways of creating a file on Linux, you can read this tutorial.
How do I edit a file in Linux using a text editor?
To edit a file in Linux using a text editor, you can use widely used text editors such as nano or vim. Open your terminal and type the following command: `nano filename` or `vim filename`, replacing “filename” with the name of the file you want to edit.
What command do I use to open a file in Linux?
To open a file in Linux, you can use the command `nano filename` or `vim filename`, where “filename” is the name of the file you want to access. Make sure you are in the correct directory or specify the absolute path.
Can I append content to an existing file in Linux?
Yes, you can append content to an existing file in Linux. Open the file using a text editor like nano or vim, navigate to the end of the file, and type your new content. Alternatively, you can use the `echo “string” >> filename` command to append a string directly from the terminal.
How do I overwrite an existing file in Linux?
To overwrite an existing file in Linux, simply open it with a text editor and make your changes. When you save the file, it will replace the old content. You can also use the `cp` command to overwrite a file with another file by specifying the new file’s name as the target.
What should I do if the file does not exist when I try to edit it?
If the file does not exist, the text editor will create a new file with the specified file name when you save it. Make sure to provide the correct file name and check your directory navigation.
How do I navigate to the directory containing the file I want to edit?
To navigate to the directory containing the file you want to edit, use the `cd` command followed by the path to the directory. For example, `cd /path/to/directory` will take you to that directory.
What if I want to rename a file in Linux?
To rename a file in Linux, you can use the `mv` command followed by the current file name and the new name. For example, `mv oldfilename newfilename` will rename the file.
Is there a straightforward way to learn how to edit files in Linux?
Yes, there are many resources available online, including tutorials and documentation for specific text editors like nano and vim. Practicing in the terminal will help you become more familiar with editing files efficiently.
How do I check the output of the content of the file in Linux?
To check the output of the content of a file in Linux, you can use the `cat` command followed by the file name, like this: `cat filename`. This will display the contents of the file in the terminal.
What are some commonly used editors for editing files in Linux?
Some commonly used editors for editing files in Linux include nano, vim, and emacs. Each editor has its own interface and features, so you may choose one based on your preference and proficiency.
How do I edit a file in Linux using a text editor?
To edit a file in Linux, you can use a widely used text editor like nano or vi. Simply open your terminal and type the following command: `nano file_name` or `vi file_name`. This will allow you to edit the content of the file directly.
What command do I use to open a file in the terminal?
To open a file in the terminal, you can use the command `nano file_name` or `vi file_name`. Replace “file_name” with the actual name of the file you want to edit.
Can I append content to an existing file in Linux?
Yes, you can append content to an existing file by using the command `echo “your string” >> file_name`. This command will add the specified string to the end of the file without overwriting its current content.
How do I overwrite an existing file in Linux?
To overwrite an existing file, you can simply use the command `nano file_name` or `vi file_name` and edit the content. When you save the changes, it will replace the current content of the file.
What happens if the file does not exist when I try to open it?
If the file does not exist, the text editor will typically create a new file with the specified file name. You can then add content to this new file and save it.
How can I rename a file in Linux?
To rename a file in Linux, use the command `mv old_file_name new_name`. This will change the name of the file to the new specified name.
What is the command to navigate to the directory containing the file I want to edit?
To navigate to the directory, use the `cd` command followed by the path to the directory. For example, `cd /path/to/directory` will take you to the specified directory.
How do I check the content of a file before editing it?
You can check the content of a file using the `cat` command followed by the file name. For example, `cat file_name` will display the current content of the file in the terminal.
Is it possible to edit a file without using a terminal?
Yes, there are graphical text editors available in Linux such as Gedit or Mousepad that allow you to edit files without using the terminal. You can simply open the application and navigate to the file you want to edit.
What should I do if I want to specify an absolute path for a file?
If you want to specify an absolute path for a file, you can provide the full path in the command. For example, `nano /home/user/documents/file_name` will open the file located in the specified directory.
