In our last article, we learned how to list packages in Ubuntu with the apt command. Today, let’s learn to use the apt command to search for a package in Ubuntu.
Linux relies on packages to deliver or install applications on a system. These packages are essentially compressed file archives. These archives are used when the user wishes to install a new application or service on their system. The packages are stored in a ‘repository’ and accessed by a package management service when required. This package management service enables the user to access, modify, and install the required packages.
Getting started
The package management service for Ubuntu and Debian-based systems is called the Advanced Package Tool. Or ‘APT’ for short. If you have been using Linux for a while, you must have seen the apt command. APT was designed to provide a user-friendly, interactive front-end for the users to manage packages.
The major reason behind the development of APT was to save new users from the complexity of using the dpkg command. APT is responsible for installing, removing, updating, and managing packages of Ubuntu and Debian-based systems.
APT was noticed by the majority in Ubuntu 16.04 and it immediately soared off in popularity. You use APT in the command line with the help of the ‘apt’ command. While the apt command offers a wide range of functionality, in this tutorial we will focus on one aspect: searching a package using the apt command.
Different ways to Use the apt Command to Search for a Package
There are instances when we need to use the apt command to search for a package to identify the package name. In such an instance, we need to take the help of the ‘search’ function of the apt tool. The apt utility provides us with three commonly used methods to check if you have a specific package in your repository. Let us go through each of these in order.
Using apt-cache search
The apt-cache search command is very common when you want to use the apt command to search for a package. It is designed to search the package name along with its metadata such as the description, dependencies, source, and version. The command returns all the packages whose name or metadata matches the specified search keyword. Following is the syntax for searching a package using the apt-cache search command.
apt-cache search [keyword]
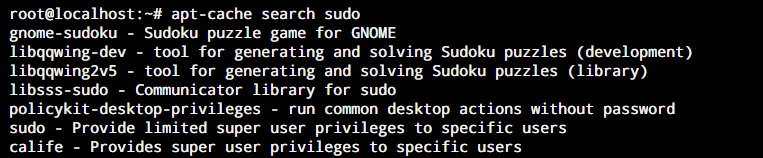
This is the older version of the search command. The newer version is the one next.
Using apt search
Another method to search for available packages in your repository is to use the apt search command. This command is designed to search all the available packages in our local repository. If found, it will return the names for all the packages whose name matches our specified search keyword. This is how the syntax for this command looks.
apt search [keyword]
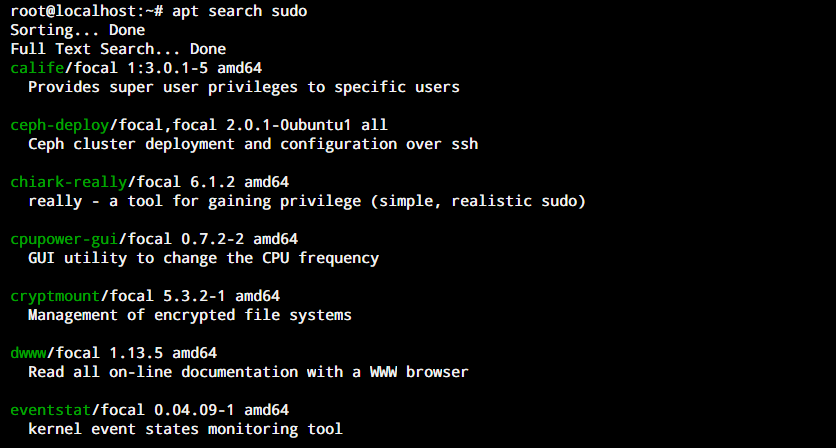
As you can see, the above screenshot shows that the data is a little more organized and visually pleasing compared to the apt-cache search output. Also it’s alphabetically arranged allowing us to see all the packages that match. The sudo package is listed close to the end of this list.
Using apt-file search
Alternatively, you can use the apt-file command. This is a command-line tool that is a part of the APT package manager. It is specifically designed to search for packages and the files stored in them as part of your repository. This command will return all the packages where the package name or any file name stored in it matches the specified search keyword. This is the syntax for using the apt-file search command on Ubuntu.
apt-file search [keyword]
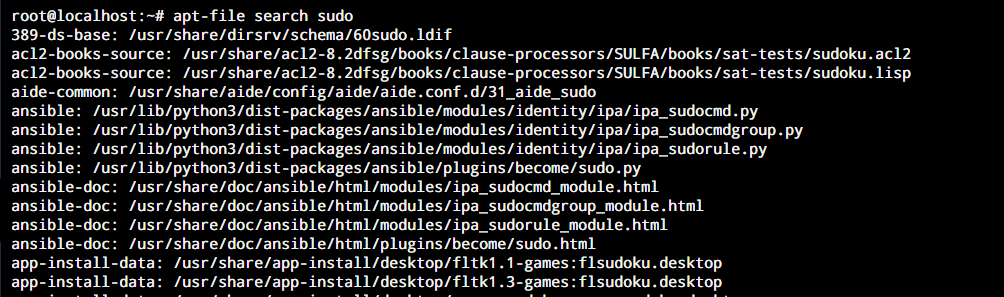
If you get an error while using this utility, you can run apt install apt-file and then do an apt-file update before beginning your search.
Wrapping up
Linux-based systems utilize packages for installing and running all kinds of applications and services. This makes it essential for a Linux user to be able to manage and keep a note of all the available packages in their local repository. Keeping a mental note of all the packages available in your repository is beyond human capacity. So thankfully, we can use the apt command to search for a package in Ubuntu.
We hope this tutorial was able to help you understand how to search for a package on Ubuntu. If you have any feedback, queries, or suggestions, feel free to reach out to us in the comments below.
How can I search for a package in Ubuntu using the apt command?
To search for a package in Ubuntu using the apt command, you can use the following syntax in the terminal: apt search. This command will display a list of packages that match the search term.
What is the difference between apt and apt-get when searching for packages?
The apt command is a more user-friendly front-end for the apt-get command. When searching for packages or specific software on a Linux distribution, you can use apt-cache search in combination with grep to locate specific items. apt provides clearer and more concise output compared to: An aspect of searching for information about packages within a Linux distribution. apt-get.
How do I specify the version of a package I want to search for using apt?
To search for a specific version of a software package using apt, you can append the version number to the package name.
Can I search for packages across different repositories using the apt command?
Yes, the terminal can execute this command. apt command searches for packages across all repositories that are enabled on your system, including the official repository as well as any third-party repositories.
How can I get detailed information about a specific package using the apt command?
To get detailed information about a specific package, you can use the: A method used to search for information about packages within a Linux distribution. apt show command. This will provide you with a description, version, dependencies, and other relevant information about the package.
Is it possible to search for packages by their description using the apt command?
Yes, you can search for packages by their description with the apt command by using the –names-only option. For example: apt search –names-only
How do I update the package cache before searching for packages with apt?
Before searching for packages using the apt command, it is recommended to update the package cache by running sudo apt update, a command to automatically refresh the system’s list of available packages to the latest versions.. This ensures that you have the most up-to-date information about available packages.
