yt-dlp is a fork of youtube-dlc with additional features and fixes of the now-inactive YouTube-dl tool, which was an open source command-line program to download videos and playlists from various websites, including YouTube. It is a really useful tool which allows you to download videos, audio and subtitle as well, at a specific resolution. You can use it to stream a video directly to your media player as well.
In this tutorial, we will take a look at the installation process of this tool and learn how to properly use it to download video, audio and subtitles, and we will also try to embed the metadata of the video into our download file.
Also Read – Watch YouTube videos in the Terminal using YTFZF tool
Installing yt-dlp
The installation process of this tool is really simple, just open a Terminal and type the following commands regardless of which distribution you use to download yt-dlp on your distro:
sudo wget https://github.com/yt-dlp/yt-dlp/releases/latest/download/yt-dlp -O /usr/local/bin/yt-dlp
sudo chmod a+rx /usr/local/bin/yt-dlp
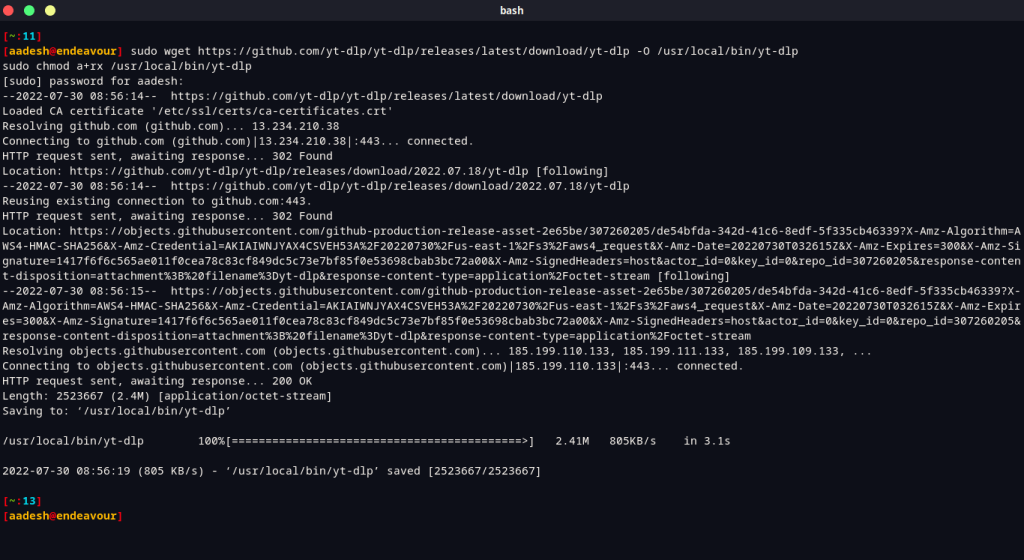
Installing ‘ffmpeg’ and ‘aria2c’ alongside yt-dlp
While the primary function of yt-dlp is to download videos, it also supports video format conversion, audio extraction, and parallel downloading of media files. To do so it required ffmpeg and aria2c tools, yt-dlp utilizes these external tools to accomplish this extended functionality.
A. Why do we need to install ffmpeg?
ffmpeg is a widely-used, open-source multimedia content processing program. It can convert video and audio formats, resize videos, and extract audio from video files, among other duties.
yt-dlp makes use of ffmpeg to:
- Convert downloaded video files to various codecs (e.g., from WebM to MP4).
- Audio extracted from downloaded video files (e.g., to create an MP3 file from a video).
- Combine audio and video recordings in formats where they are downloaded separately (e.g., DASH formats on YouTube).
B. Why do we need aria2c in ytdlp?
‘aria2c’ is an open-source, lightweight download utility that supports multiple protocols and parallel downloads.
Here’s how aria2c gets used by yt-dlp as an external encoder as well as external downloader for the following tasks,
- Using multiple connections for a single file to download files expedites the process.
- Allow simultaneous downloads of multiple media assets.
- Offer more sophisticated distribution management options.
While ffmpeg and aria2c are not required for fundamental video downloading with yt-dlp, they are required for additional features and improved performance. These utilities improve the overall functionality and user experience of yt-dlp when installed.
Once the installation is finished, you can start using it, the usage is discussed in the next section.
Using the yt-dlp tool
Just like any other command on Linux, this one too follows the command [options] format. To download a video, type it like this along with the URL :
yt-dlp -f 'bv*+ba' https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aqz-KE-bpKQ
Here, the -f argument signifies ‘format’. This command will automatically download the best quality video and audio format available for this particular video. However, to download this video in a specific quality, let’s say 1080p, you can use the following arguments :
yt-dlp -f 'bv*[height=1080]+ba' https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aqz-KE-bpKQ

As you can see in the properties of the video file, the downloaded video is in 1080p quality instead of the highest 4k. Similarly, you can use a playlist URL in order to download multiple videos at the same time.
Modify the configuration file for better usage
You can set up various kinds of defaults for this tool which it will automatically use, such as a preferred video format (mkv, mp4, webm) or SponsorBlock marking/removal etc. To create the config file, type the following in your Terminal :
# For vim editor users
sudo vim /etc/yt-dlp.conf
# For Nano editor users
sudo nano /etc/yt-dlp.conf
Once the file is created, you can add various configurations to it, for example, mine looks like this :
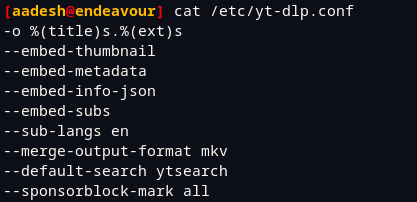
Save and exit in the vim editor by pressing the escape key and type :wq to exit, in the nano editor press Ctrl+O and Ctrl+X. Using the above configuration, yt-dlp will automatically embed thumbnail, metadata, English subtitles and SponsorBlock segments into the video automatically. And due to the first line, the video will be renamed to Title.extension instead of Title-URL.extension which is the default. –merge-output-format mkv option will download the video directly into mkv format.
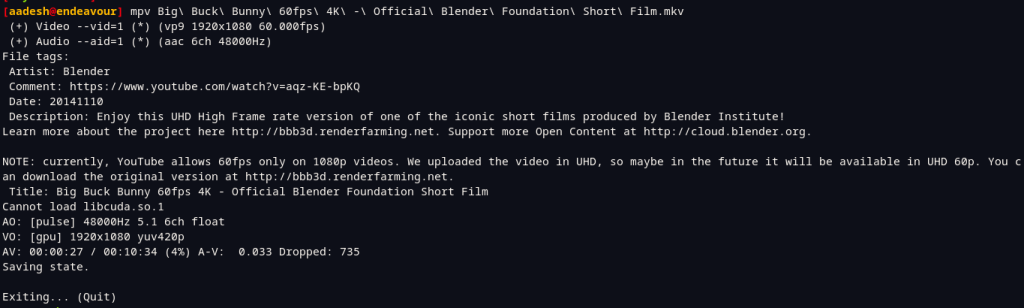
When you play the video via the command line, you can see all the metadata associated with the video.
One more thing, you can play with is the bashrc file of your system to avoid typing big commands every time. Open .bashrc file by typing :
# For Vim users
vim ~/.bashrc
# For Nano Users
nano ~/.bahsrc
I’ve set the following alias, you can add it too :

Now, when I type ytdl <Link>, the first command will be executed along with all the configurations we’ve set in the config file. And audio command will download the audio from a link into a mp3 container. Don’t forget to refresh the bashrc file by typing :
source .bashrc
The final result should look something like this :
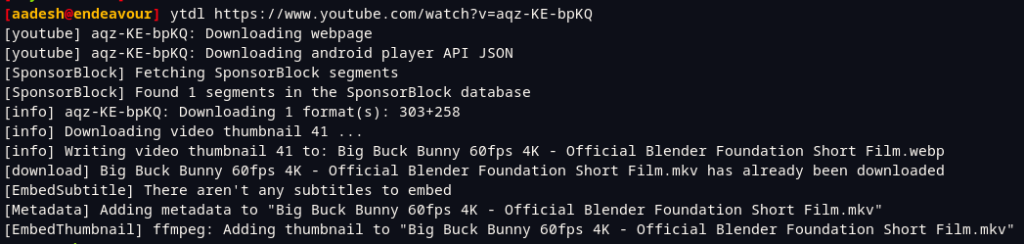
Summary: A Modern YouTube-dl fork to download videos from YouTube
There are more cool features available for this tool which I have not described here, you can check out official GitHub page of this project for more information. Of course, there is a question of whether downloading YouTube videos count as piracy or not. Well, if you do it for data hoarding processes and do not make any kind of profit while downloading/distributing it, I don’t think It’s wrong. However, you should check the copyright laws in your Country before making any decision.
References
Read more on aria2c from their official site.
