Files and directories are the building blocks of any Operating System like Linux; knowing what kind of file we are working with is crucial before we open or execute the wrong kind of file. You could be a developer accessing a large codebase, a system administrator troubleshooting issues, or a Linux enthusiast navigating through the beautiful terrain of the Linux ecosystem; Chances are high that you have encountered almost all of the file types there are, such as text files, executables, images, audio files, etc.
How do we distinguish between each of these file types? especially when Linux doesn’t rely on file extensions for identification!
Fret not! The Linux terminal has blessed us with a pretty nifty command-line-based tool called the ‘linux file command’. It serves as your digital sherlock, unearthing valuable information about files with simple instructions.
In this article, we will explore the Linux file command in depth, covering its syntax, options, and real-world applications. By the end of this guide, you’ll have mastered the art of file identification in Linux, making our journey through the Linux filesystem easier and more efficient.
What is file command in Linux?
The file command in Linux is used to determine the type of file we are working with. Unlike in other OSes where the file type is determined by its extension (e.g., .txt for text files, .jpg for JPEG images), Linux does not rely on file extensions to determine a file’s type. Instead, it runs a couple of tests to understand the file’s contents and it’s attributes.
So when we run the file command on a file in Linux, the command performs the following tests, which can be broadly categorized into filesystem tests, magic tests, and language tests. The first test to pass usually determines the file type.
Various tests performed by the file command in linux
1. Filesystem Tests
The first thing that the file command checks are the filesystem attributes of the file. This includes:
- File Type: Whether the file is a regular file, directory, symbolic link, socket, etc.
- Permissions: Since permissions affect the ability to read the file.
2. Magic Tests
The magic tests are comprehensive and are based on a “magic” number, which is a unique identifier at the beginning of the file. The file command stores a database of these magic numbers and their corresponding file types.
Here’s what it does:
- Magic Number: Reads the first few bytes of the file to identify this unique identifier.
- File Header: Some files have specific headers that help in identification.
- Binary Patterns: For executable or compiled files, specific binary patterns can be indicative of the file type.
The magic tests are quite reliable for identifying file types like images, executables, and more.
3. Language Tests
If the file in question doesn’t pass the magic tests, the file command then moves on to language tests. These are particularly useful for text files. The command will check the following,
- Character Encoding: Determine the character set used in the file, such as ASCII, UTF-8, etc.
- Text Patterns: Look for specific text patterns that might indicate a scripting language like Python, Perl, or a markup language like HTML.
- Line Endings: The type of line endings (CR, LF, CRLF) can sometimes also be a clue, especially to distinguish between Unix and Windows text files.
These tests are highly-useful for text-based files like scripts or documents.
By combining the results of these tests, the file command provides a comprehensive and reliable way to identify almost any file we might encounter in a Linux environment.
Syntax of the File Command
The basic syntax of the file command is:
file [options] filename
Here’s an example of the file usage,
$ file filename
Linux File Command Options
There are various other options used with the file command. Here’s a quick list of the commonly used file command options in Linux:
| Option | Function |
| file * | Lists all the files in the system |
| file <directory>/* | Lists all the filetypes present in a specific directory |
| file -b or –brief | To get a short description of the file |
| file -c | To get the parsed form of any file |
| file -F | Specifies a custom separator between the filename and its type. |
| file -i | Outputs the MIME type of the file. |
| file -z | To view details of compressed files |
| file <space separated filenames> | Lists the types of multiple files specified. |
| file –help | To get the complete manual |
Following are some examples of the file commandin action,
Get a Brief Description
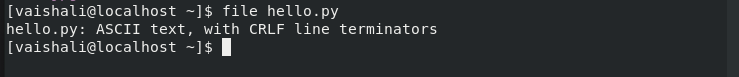
-b or –brief option is used with the file command to get a brief description of any file. It would only display the file type without its name.
$ file -b hello.py
List the Type for All the Files
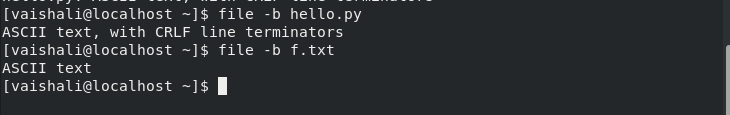
This command is used to display the types of all the files or directories. The file command uses '*' to list the types of all the files in the system.
$ file *
File Command using Directory Names
This command is used to display all filetypes in a particular directory.
$ file B2/*

Listing File Types using Regex Style Ranges
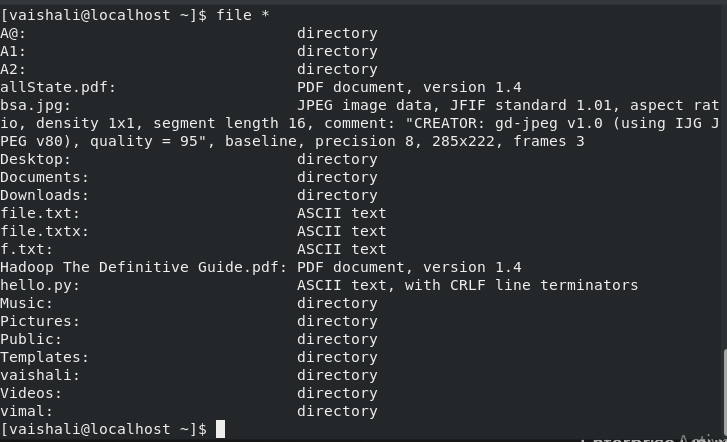
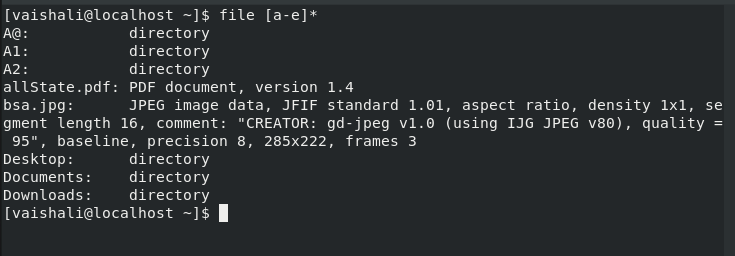
This command is used to display file types of files in a specific range. Select the range i.e from A to Z or A to F, it can be anything. It will display only those names that are in range.
$ file [a-e]*
Using -c option
This command option is used to print the parsed form of any file i.e type, opcode, value, mask and so on.
$ file -c

Custom Separator For File Type Output
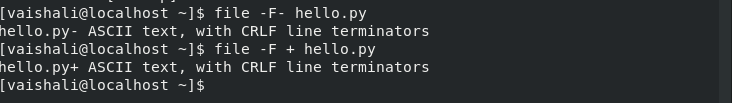
As you may have noticed above, the file name and file type is separated with a colon :. To change this separator in the output, you can use the -F option. The -F option followed by the separator will change the default separator, as shown in the image below.
$ file -F - hello.py
$ file -F + hellp.py
Find File MIME Type Using File Command
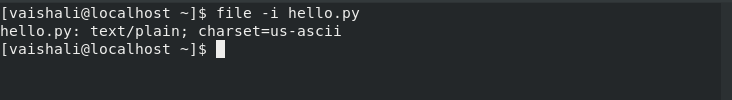
This command is used to view the mime type.
$ file -i hello.py
Display Compressed File Types
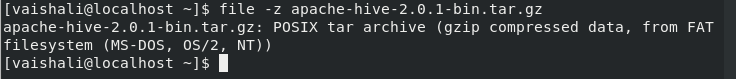
The -z option for the file command will give us the details of an archive file.
$ file -z {compressed file name}
Here’s an article that covers how to extract the compressed files in detail.
Display Types for Multiple Files
We can enter multiple file names separated by a space to display the file types for them at once. Have a look at the example below.
$ file f.txt .local Desktop
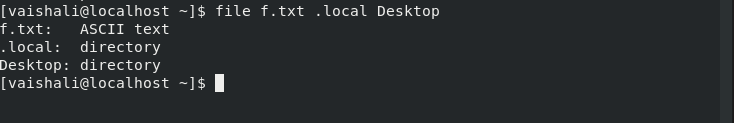
Here, f.txt, .local, and Desktop are file names.
Help Command Option
This command is used to get a list of all the options that are available for the file command.
$ file --help
Alternatively, you can also use the man command in Linux to get detailed help on the file command.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve gone over the syntax, options, and real-world applications of the file command, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the Linux filesystem more efficiently.
Mastering the file command is essential for effective file management and system navigation.
We hope this article has helped you understand and learn how to use the command efficiently.
References
Check this Linux Documentation on File Command.
