Find command is used to filter objects in the file system. It can be used to find files, directories, files of particular pattern i.e. txt,.php and so on. It can search by file name, folder name, modification date , by permissions and so on.
$ find [where to start searching from] [-options] [what to find]
Note:
Linux is case sensitive. “File”,”file”,”FiLe”,”FILE” all are different file names in the Linux file system.
Lets have a look on various options used with find command.
Consider the tree hierarchy:
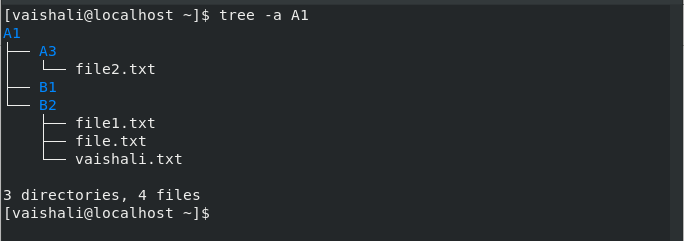
There are some commonly used commands which are described based on this hierarchy.
- -name: used to search a particular file.
- -exec CMD: the file is searched as per the given condition, returns 0 as its exit status.
- -inum N: search for the file having inode number N.
- -links N: search for the file having links ‘N’.
- -newer file: search for the file names that are modified after “file”.
- -perm octal: search for the files if the permission is ‘octal’.
- -print: print the path of the file listed.
- -empty: search for the empty files or directories.
- -size +N/-N: search for the files of size ‘N’.
- -user name: search for the files with user name or owned by the user.
- -rm file: search for the file and removes it.
Find command with -name option
This command searches file with a particular name.
$find ./A1 -name file1.txt

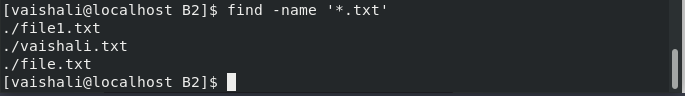
Searching file of a pattern
This command finds a file of a particular pattern such as .php, .txt and so on.
$find -name '*.txt'
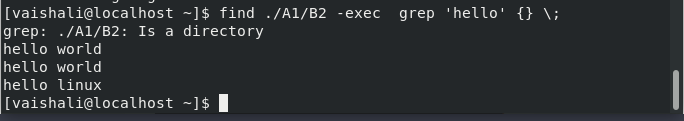
Find with -exec option:
This command returns the status for successful command execution according to the condition.
In this example, the command will print lines that have a “hello” keyword in it. Grep keyword is used to find words in files.
$ find ./A1/B2 -exec grep 'hello' {} \;
Find file with -inode no.
An inode is a data structure on a traditional Unix file system. It is denoted as the indexing of files.
-inum command is used to search for the files having inode number ‘N’.
To find -inode number, the command is :
$ ls -id /path to dir
To find the file with particular inode number, the command will be:
$ find ./A1/B2 -inum 42032

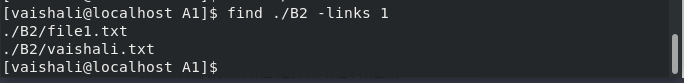
Find links using -links option
This command is used to search for the files with ‘N’ links
$ find ./B2 -links 1
Linux Find -newer option
This command is used to search for the files that were modified after the ‘file’ (it can be any file).
$ find -newer file.txt

It will print the file names that were modified after ‘file.txt’.
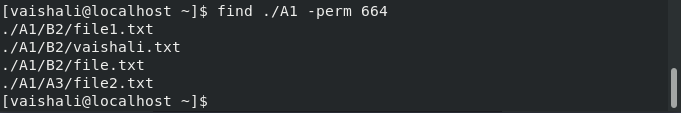
Linux Find -perm option
This command searches for the file which has ‘octal’ permission.
$ find ./A1 -perm 664
Print the path of a file
This command is used to print the path of the directory or file.
$ find -print
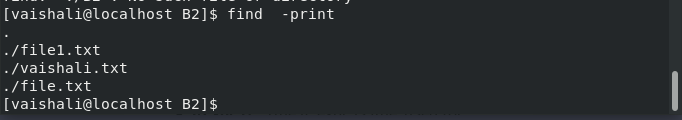
Here, it will print the path of the file in B2 directory ( consider the tree hierarchy as shown above)
Find empty files
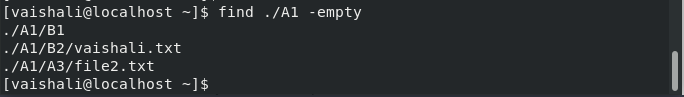
This command is used to search for empty files or directories.
$ find ./A1 -empty
Search files of a particular size
This command is used to search for the files having size ‘N’
$ find ./B2 -size 0M

Linux find -user name option
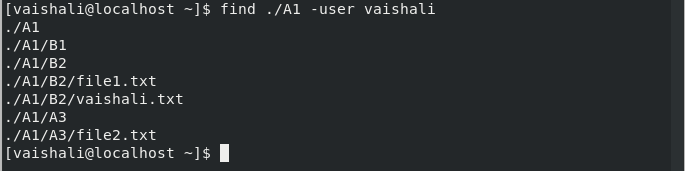
This command search for the files owned by the user name or id ‘name’.
$ find ./A1 -user vaishali
To remove files or directories
This command is used to remove the file from a directory.
$ find ./A1 -name "file.txt" -exec rm -f {} \;
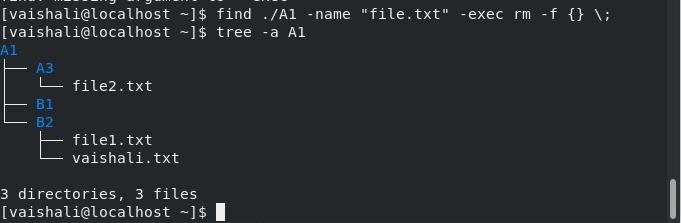
These are the commands which can be used to search file or directories.
Conclusion
We hope that you now have a proper understanding of the find command. If you have any questions, do let us know in the comments below.
