We often store duplicate files in our directory, whether music or documents. Deleting those files is very exhausting, especially when you don’t know which files have more than one copy. That’s where the fdupes command comes in. In this article, we will go through the installation process of this tool, and we will also learn how to use this.
What is fdupes?
Fdupes is a command line utility that identifies duplicate files by several methods one by one for you. First, it looks at the files and compares their size followed by a partial MD5 signature comparison and then a full MD5 signature comparison, and at last, this performs a full-byte-to-byte comparison between two files. This utility is written in C programming language by Adiran Lopez.
Installing fdupes on Linux distributions.
This application is available in the official repositories in every Linux distribution, so the Installation procedure becomes easy. Just open a Terminal and then type the following commands, depending on your Linux distribution :
# On Debian and Ubuntu-based distributions
sudo apt update && sudo apt install fdupes
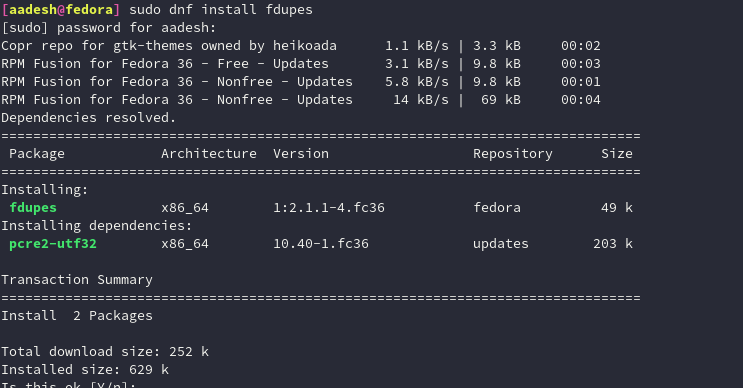
# On Fedora Workstation
sudo dnf install fdupes
# On Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S fdupes
Usage of fdupes
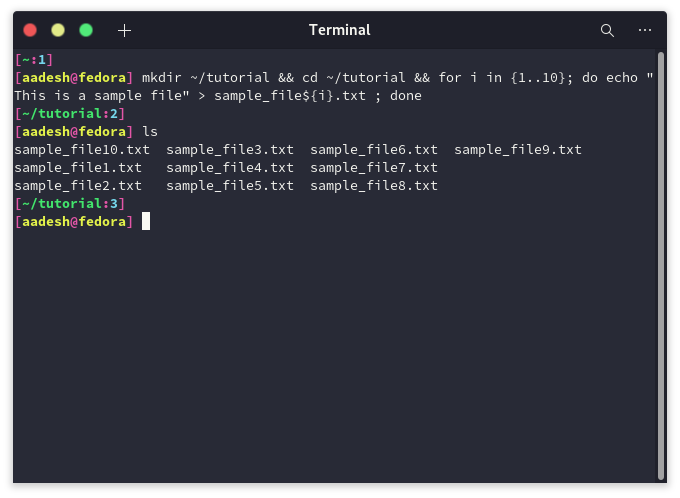
I’m going to create several duplicate files for demonstration purposes of this tutorial, you can use them directly though.
mkdir ~/tutorial && cd ~/tutorial && for i in {1..10}; do echo "This is a sample file" > sample_file${i}.txt ; done
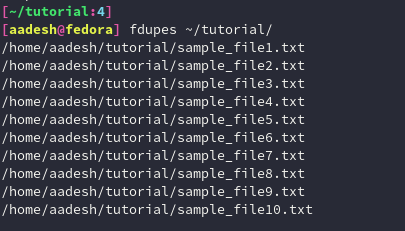
Now, let’s search for duplicate files using the fdupes command:
fdupes ~/tutorial
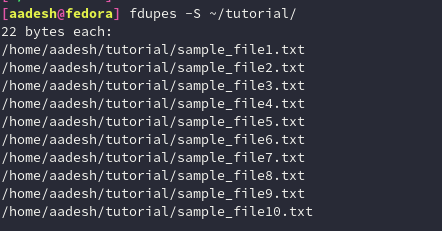
You can also search for duplicate files recursively within subdirectories using the -r flag. Using the -S option, you can also list out the size of all the files.
Finally, to delete the duplicate files using this command, you can use the -d option. Be careful, always perform a double check so that you don’t lose your data. Enter the range of files to PRESERVE and then press enter to mark your selection.
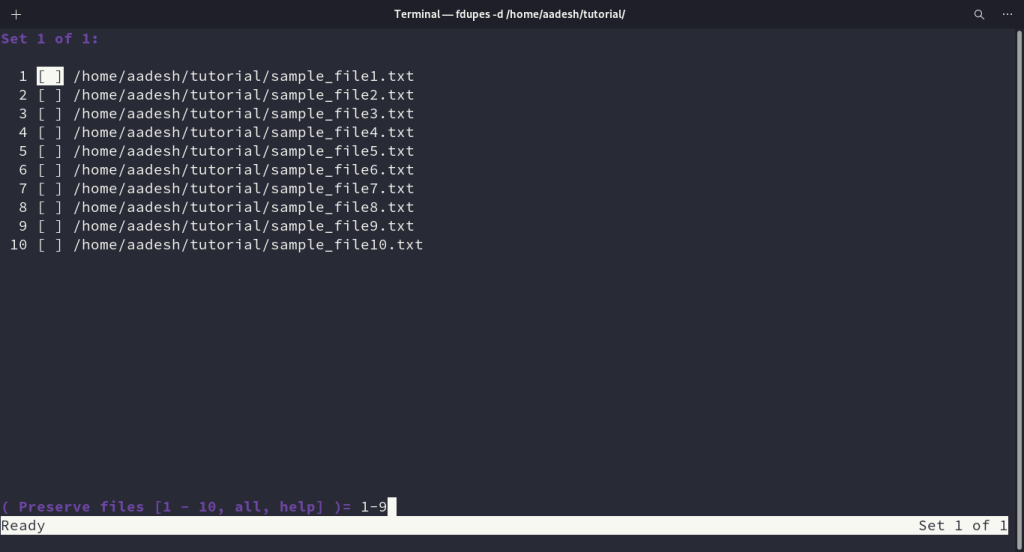
After tagging the files, you can type prune and then press enter to delete all the unmarked (-) files.
Summary
This is a lightweight, handy little tool that will save you a lot of time in the long run. You can look up more options of the fdupes command by typing the following command if you get confused about anything.
fdupes -h
References
What is fdupes and how does it help in managing duplicate files?
fdupes is a command-line tool used in Linux to find and delete duplicate files. It helps in efficiently organizing your files by identifying duplicate copies and allowing you to manage them effectively.
How can I find duplicate files in Linux using fdupes?
To find duplicate files in Linux using fdupes, you can simply run the command ‘fdupes’ followed by the directory you want to scan for duplicates. fdupes will then list all the duplicate files found in that directory.
Does fdupes provide the option to delete duplicate files?
Yes, fdupes allows you to not only find duplicate files but also gives you the option to delete them. You can use the appropriate flags with the fdupes command to set the action to delete duplicates.
How does fdupes identify duplicate files?
fdupes uses the MD5 signature of files to identify duplicates. When scanning a directory, fdupes calculates the MD5 hash of each file and compares them to determine if any files have the same MD5 signature.
Are duplicate files listed together when using fdupes?
Yes, when fdupes finds duplicate files in a directory, it lists them together for easy identification. This allows users to view all duplicate copies in one place and take necessary actions accordingly.
How can I exclude zero-length files from consideration when using fdupes?
To exclude zero-length files from consideration when using fdupes, you can use the ‘-n’ or ‘–noempty’ flag with the fdupes command. This ensures that only non-zero-length files are considered for duplicate detection.
Where can I refer to the fdupes documentation for additional information?
For additional information on fdupes and their functionalities, you can refer to the fdupes documentation. It provides detailed explanations of various flags, options, and usage scenarios to help you make the most of fdupes.
